Bed bugs can be difficult to detect, but there are some signs you can look to determine if you have an infestation.
It’s important to find a bed bug infestation early, before it becomes a bigger problem. If you catch it early, it’s easier and less expensive to get rid of. So, it’s a good idea to check for bed bugs regularly, especially if you’ve been traveling or staying in a new place. Don’t wait until the infestation gets worse before taking action.
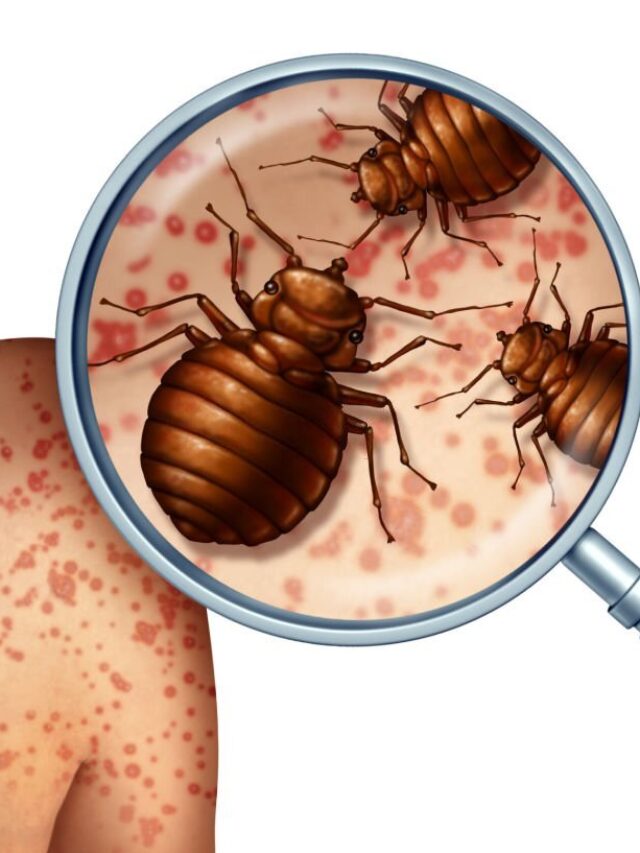
Bites on the skin are a poor indicator of a bed bug infestation. Bed bug bites can look like bites from other insects (such as mosquitoes or chiggers), rashes (such as eczema or fungal infections), or even hives. Some people do not react to bed bug bites at all.
Here are some ways to find bed bugs:
1. Look for physical evidence: Bed bugs leave behind physical evidence, such as tiny blood spots on your sheets or mattress, as well as shed skins or exoskeletons.
2. Check for bites: Bed bugs bite humans, and their bites often appear in clusters or lines. If you wake up with unexplained bites, it’s possible that bed bugs are the cause.
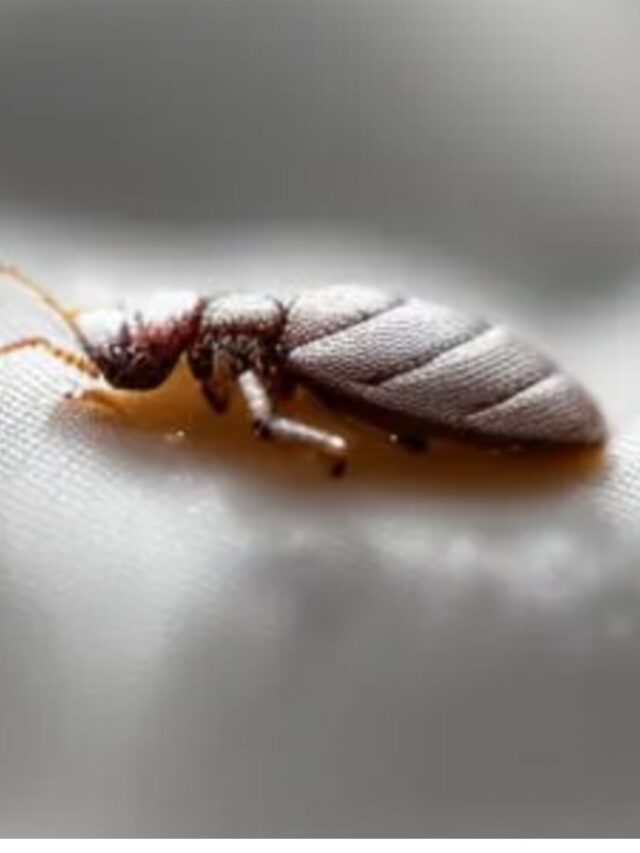
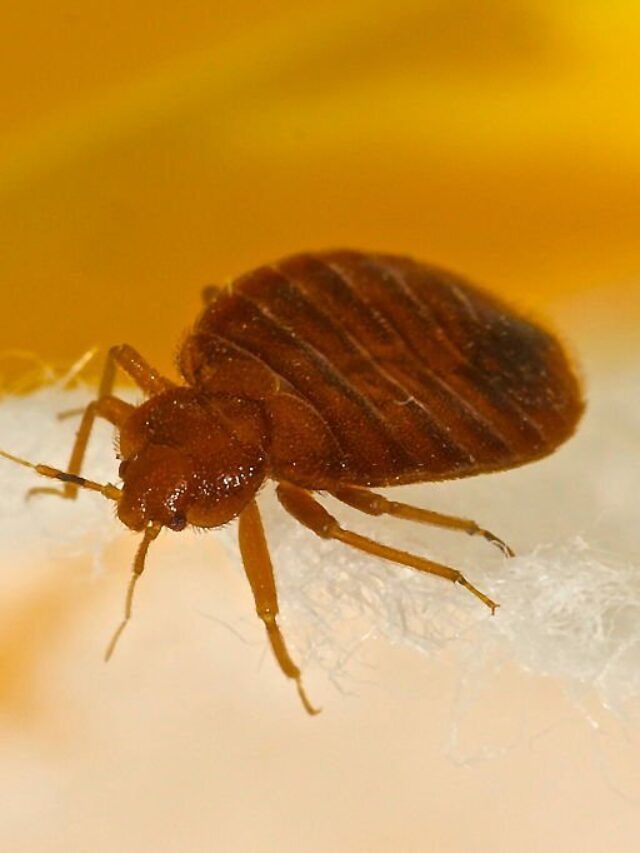
3. Look for bugs: Bed bugs are small, flat, reddish-brown insects that are about the size of an apple seed. Check your mattress seams, bed frame, headboard, and nearby furniture for signs of the bugs.
4. Use a flashlight: Bed bugs are nocturnal and typically hide during the day. Using a flashlight to inspect your bed and furniture at night may make it easier to spot them.
5. Use interception devices: You can purchase interception devices, such as sticky traps or climb-up interceptors, to place under the legs of your bed or nearby furniture. These devices can trap bed bugs and help you determine if you have an infestation.
It’s important to note that bed bugs can be difficult to eliminate, so if you suspect an infestation, it’s best to contact a professional pest control company for assistance.
Signs of Bed Bugs
A more accurate way to identify a possible infestation is to look for physical signs of bed bugs. When cleaning, changing bedding, or staying away from home, look for:
1. Rusty or reddish stains on bed sheets or mattresses caused by bed bugs being crushed.
2. Which are bed bug excrement and may bleed on the fabric like a marker would.
3. Eggs and eggshells, which are tiny (about 1mm) and pale yellow skins that nymphs shed as they grow larger.
4. Bite marks on your skin that may appear in a line or cluster, often with a red spot in the center.
5. Blood stains on your sheets or pillowcases, which may result from accidentally crushing a bed bug while you sleep.
6. Dark or rusty spots of bed bug excrement on your bedding, mattress, or nearby walls.
7. A musty odor, which can come from the bed bugs’ scent glands.
8. Visible bed bugs themselves, which are small, flat, and reddish-brown in color. They can often be found hiding in cracks and crevices, such as the seams of your mattress or in the folds of your bedding.
If you suspect that you have a bed bug infestation, it’s important to take action as soon as possible to prevent the problem from getting worse. You may want to consult with a pest control professional to help you identify and treat the infestation.
Where Bed Bugs Can Hide ?
Bed bugs are very skilled at hiding and can be found in many different places. Here are some common places where bed bugs may hide:
1. Mattresses and Box Springs: Bed bugs love to hide in the seams and folds of mattresses and box springs, as well as in the tufts and buttons.
2. Headboards and Bed Frames: Bed bugs may also hide in the cracks and crevices of headboards and bed frames.
3. Furniture: Bed bugs can hide in couches, chairs, and other upholstered furniture. They may also hide in wooden furniture such as dressers and nightstands.
4. Baseboards and Electrical Outlets: Bed bugs may hide in the cracks and crevices of baseboards and electrical outlets.
5. Luggage and Clothing: Bed bugs can easily hitchhike in luggage and clothing, so be sure to thoroughly inspect these items when traveling or after staying in an infested location.
6. Carpets and Rugs: Bed bugs may also hide in carpets and rugs, especially if they are close to the bed.
7. Walls and Ceilings: Although less common, bed bugs may also hide in the cracks and crevices of walls and ceilings.
It’s important to remember that bed bugs are very small and can hide in spaces as thin as a credit card. Be sure to thoroughly inspect all possible hiding places if you suspect a bed bug infestation.
Habits And Behaviour Of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are parasitic insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. They are reddish-brown in color and about the size of an apple seed when fully grown. Bed bugs are nocturnal and typically feed at night, making it difficult to detect their presence. Here are some habits and behaviours` of bed bugs:
1. Feeding Habits: Bed bugs feed on blood, typically from humans, but they can also feed on the blood of animals. They are attracted to the carbon dioxide and heat that humans and animals emit, which is why they prefer to feed at night when their hosts are asleep. Bed bugs use a long, straw-like mouthpart called a proboscis to pierce the skin and suck blood for several minutes. They can go several months without feeding, but they prefer to feed every five to ten days.
2. Reproduction: Bed bugs reproduce by mating, and females can lay up to five eggs per day. The eggs are about the size of a pinhead and are typically laid in cracks and crevices near a food source. The eggs hatch in about ten days, and the nymphs that emerge resemble adult bed bugs, but are smaller and lighter in color.
3. Movement: Bed bugs are not good at flying, but they are excellent at crawling. They can crawl up walls, across ceilings, and even across floors. They are also very good at hiding in small cracks and crevices, making them difficult to detect.
4. Aggregation: Bed bugs are known to aggregate in certain areas, which is why infestations can quickly grow out of control. They prefer to hide in small spaces such as cracks and crevices, and they often aggregate in areas where their hosts spend a lot of time, such as on or around beds and couches.
5. Sensitivity to Temperature: Bed bugs are sensitive to temperature and prefer temperatures between 70 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit. They can survive in a range of temperatures, but extreme heat or cold can kill them. This is why heat treatments and freezing treatments are often used to control bed bug infestations.
6. Travel: Bed bugs are very good at catching rides and can move easily from one place to another by sticking to suitcases, clothes, and other things we carry. They often hang out in hotels and places where people stay while traveling, so it’s important to check your belongings for bed bugs after staying in a place that might have them.
7. Detection: Bed bugs are difficult to detect because they are small and often hide in cracks and crevices. However, there are some signs of bed bug infestations that homeowners can look for, such as blood stains on sheets and mattresses, dark spots (bed bug feces) on mattresses and furniture, and a sweet, musty odor.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bed bugs are parasitic insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. They are nocturnal and prefer to feed at night, making it difficult to detect their presence. Bed bugs reproduce quickly and are known to aggregate in certain areas, making infestations difficult to control. Homeowners should be vigilant about detecting bed bugs and taking action quickly to prevent infestations from spreading.